Concepts and use of data
The concepts of working with data in Bliksund Analytics is based on a Medallion architecture, which is commonly used when working with data. It will help you manage and process data efficiently, ensuring high data quality and facilitating various types of analytics. Here is a detailed descriptions of the different layers.
Step-by-Step description
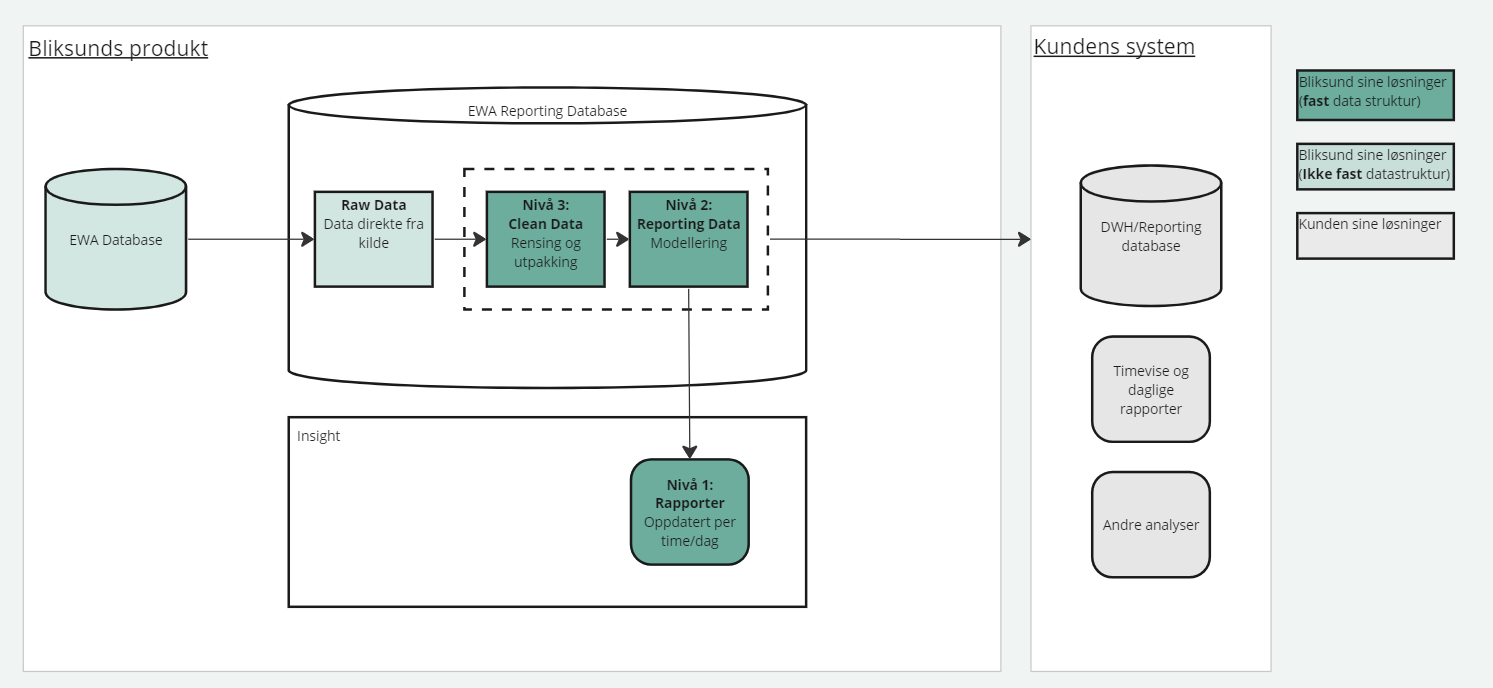
Data Ingestion (Raw Data Layer)
- Purpose: Store raw, unprocessed data.
- Data Processing: No data processing
- Characteristics: Data is in its original format, often including duplicates, missing values, and inconsistencies.
- Usage: Acts as a staging area for raw data, useful for auditing and reprocessing.
- Use Case: Should not be used in pipelines, as the structure might change, but can be used to investigate data directly from source
Data Processing and Cleansing (Clean Layer)
- Purpose: Store cleansed and partially transformed data.
- Data Processing:
- Cleaning: Removing duplicates, handling missing values, and correcting errors.
- Basic Transformations: Standardizing formats, filtering out irrelevant data, and performing straightforward enrichment.
- Characteristics: Data quality is improved and structured, making it more reliable for analysis while still flexible for further processing.
- Usage: Suitable for intermediate analytics and as a source for more specific transformations and aggregations.
- Use Case: Customers who need semi-processed data for more complex and customized data modeling and transformations.
- Benefits:
- More flexibility to perform custom transformations and analyses.
- Access to cleansed and enriched data, reducing the need for extensive data cleaning.
- Suitable for customers with data engineering capabilities.
- Drawbacks:
- Requires customers to have a good understanding of data processing.
- Might involve more storage and compute resources on their
Data Aggregation and Enrichment (Core Layer)
- Purpose: Store aggregated and highly curated data.
- Data Processing:
- Advanced Transformations: Aggregations, summarizations, and applying business logic.
- Optimization: Ensuring data is ready for performance-intensive reporting and analysis.
- Characteristics: High-quality, ready-to-use data, optimized for specific business needs.
- Usage: Used for business intelligence, advanced analytics, and reporting, providing end-users with actionable insights.
- Use Case: Customers who need high-quality, ready-to-use data for reporting and analytics.
- Benefits:
- Data is highly curated and optimized for reporting, making it easier to use.
- Reduces the complexity for customers, as the data is already aggregated and summarized.
- Ideal for business users and analysts who need quick access to insights without deep technical skills.
- Drawbacks:
- Less flexibility for customers who need to perform custom data transformations.
- Might not cover all specific use cases that customers have, as it’s more tailored to common reporting needs.